Angela Brett
Mathematician and linguist by training, programmer by trade, physicist by association, writer by neglecting everything else.
Homepage: http://angelastic.com
We did a Christmas
Posted in Holiday Highlights on December 26, 2023
I’m visiting Joey Marianer for Christmas, so we sang a slowed-down cover of a Worm Quartet song, as Joey is wont to do.
Worm Quartet is also known as Timothy F. Crist, so we wished everyone a merry Timothy F. Cristmas at the end. I hope you had one of those, whatever it means. I don’t see why anyone wouldn’t celebrate such a talented comedy musician.
I did actually try some of that eggnog (‘milk that have a alcohol and then we put a egg’ except that this one didn’t have a alcohol.) The few times I’ve had eggnog before, I’ve thought that the alcohol ruined what could have been a very nice drink, so I was excited to try some non-alcoholic eggnog. Not only that, but I tried it mixed with orange soda, as recommended on the Judge John Hodgman podcast. I really like it both ways! It’s also good with orange juice.
In unrelated news, we went to the MathsJam Annual Gathering, where Joey gave a talk on the true prisoner’s dilemma, and at MathsJam Jam we sang Symmetry and Seven Bridges (of Königsberg) Road. Ben Sparks taught everyone the harmonies for the Eagles version of Seven Bridges Road to sing Seven Bridges (of Königsberg) Road, and it was fantastic.
We didn’t sing This Tiling Never Repeats, because nobody (not even me) knew the music well enough. But on the Saturday of MathsJam, Joey and I wore Cirque du So What ‘I Want TILE!’ shirts, and I did in fact come away with a few handfuls of 3D-printed spectre aperiodic monotiles. Surprisingly, there were no aperiodic monotile shaped baked goods in the MathsJam BakeOff.

This Tiling Never Repeats (Split Enz parody)
Posted in News on October 29, 2023
I mentioned in a previous post that I was working on a parody of History Never Repeats, by Split Enz, about the aperiodic monotiles that have been found recently. I’ve finished it, so here are the lyrics:
This tiling never repeats
Unending plane the kite and dart complete
We wish to show we can improve
We may assume, there’s always more to prove
It was the best we used to know
From David Smith, a savage blow
Penrose is great, but now we sing
A monotile beats his tiling!
This tiling never repeats
But some might say, reflected tiles are cheats
We wish to show we can improve
We may assume, there’s always more to prove
You say we’ve all been played for fools
We can’t reflect, if that’s the rule
Better to work than make dispute
They made a change and now it’s moot
This tiling never repeats
There’s not a need the Spectre doesn’t meet
And there’s a way to make more and more
Leading us to a space we can explore
This tiling never repeats, this tiling never repeats
Infinite shapes, just turn the dials
Aperiodic monotiles
Pick one and all the plane is spanned
We think at last we understand
This tiling never repeats
A manifold with manifold defeats
And there’s a way to make more and more
Leading us to a space we can explore
Never repeats!
Never repeats!
Never repeats!
This joins Symmetry and Seven Bridges (of Königsberg) Road in Joey’s and my submissions for this year’s MathsJamJam. Joey Marianer (yes, the one that I’ve somehow ended up married to!) also sang (and sent for inclusion in the Jam) Polygon Pam, a parody of The Beatles’ Polythene Pam written by Chella Quint:
I look forward to seeing Joey at MathsJam (and then Chella afterwards) and singing them together! I also look forward to eating some aperiodic monotile confections which will inevitably be baked for the MathsJam BakeOff.
I mentioned in a different post that Joey had been working on some cover songs which I was excited to share. The one I was most excited about is a slow cover of Entire Dog by Worm Quartet. It lasts almost twice as long as the rather frenetic original, and Joey initially sang it this way completely off-the-cuff one day over FaceTime. After a few slight revisions, I declared it was so good it should be stolen and used on Glee. But Joey kept singing it to me and making it even better.
If you think Joey made a mistake with some SI prefixes, read the video description. To really tie the post together, here’s a slow cover of a frenetic Worm Quartet song that also mentions math — and other kinds of multiplication… let’s just say it’s NSFW — Tired Of Not:
Both of these songs are on Worm Quartet’s new album, Carpe Tedium, which I highly recommend. Joey has been practising genre-benring covers of several more tracks from it, too.
The “The Captain’s Wife’s Lament” Lament, and Seven Bridges (of Königsberg) Road
About a week ago, me hearty Joey Marianer recorded three songs (two of which I wrote) while I slept! I meant to post about them on Talk Like a Pirate Day, but ended up not being home all day. Nonetheless, I’ll start with the pirate shanty. This might not make much sense to you if you’re not familiar with Paul and Storm; it’s a parody of one of their songs, about the lengthy live performances of another of their songs, which would be less than three minutes if they had a few other singers keeping them in line.
Storm DiCostanzo, please sing, and sing faster!
You’re not going to get any younger, you know.
Hey, Paul Sabourin, we’re growing impatient,
And you’ve still got most of the song left to go,
so come on Storm, spit it out.
I curse the day that these guys ever wrote this —
a joke about seamen that’s not hard to get.
How could I know that their seed would get into
my hair and my craw and two thirds of the set
Now three lines in, and I arrr with the masses,
Dejected, excited, and counting to pi.
And I have to admit, if you’d ask to continue
my bladder says ‘no’ but my mouth says ‘aye-aye!’
Why does every new verse of your song
Keep taking you so goddamn long?
Storm DiCostanzo, please sing, and sing faster!
Enough with the jokes that we don’t understand.
I need to pee and it’s no longer funny.
Yes, that’s your R Kelly goddamn cover band.
So come on Paul, spit it out.
Eighty-six seconds for all Lehrer’s Elements,
One Week’s three minutes and Yesterday’s two.
Cohen wrote hundreds of draft Hallelujahs
but won’t subject crowds to much more than a few.
You’re not our bitches, you’re not the CD,
and we don’t mean to tell you you do your job wrong,
but please bear in mind, in the time that you’ve had
Mister Boggia churned out thirty-five Beatles songs. [actually 25]
And if you keep singing so slow,
you’ll hold up the closing band’s show!
[extract from Nobody Loves You Like Me, by Paul and Storm’s usual closing band, Jonathan Coulton]
Here at the bar who cares what I do
I’m all alone but I’m drinking for two
Drowning the man that I used to be
Nobody loves you like me
Hey, Paul Sabourin, please sing, and sing faster,
though we won’t stop arrring till long past the show.
Crap out the verses, and Storm, while he’s at it,
your G-string is tuned half a Boggia too low.
So come, yes come…
Hey Paul and Storm, please just sing, and sing faster
Don’t hold back your seamen, please spit it all out.
Mister Boggia is Jim Boggia, who is known not only for his original songs and Beatles covers, but also for having perfect pitch and being very good at tuning. The ‘Boggia’ mentioned at the end is a unit of measurement defined on JoCo Cruise 2015 as “the smallest unit of tuning perceptible only to Jim Boggia”.
The other song of mine that Joey sang is Seven Bridges (of Königsberg) Road, which I mentioned in my last post:
Joey sang it based on Steve Young’s original version, rather than the Jonathan Coulton, Paul and Storm, and Sara Watkins version that I’m familiar with. Joey is wearing a T-shirt printed with the cover of my poetry album Wake Up Gasping. The album cover is by CamannWordsmith, who makes several of the major art food groups.
The other song Joey recorded that night was a parody of ‘You’ll be back’ from the musical Hamilton, from the perspective of GlaDOS from the game Portal. It was written by Brian Young, whom I knew from the olden days of the JoCo forums (which I am surprised to see are still up), and we both know from the JoCo Cruise.
The wardrobe and impetus to learn the tune was provided by our friend Chella Quint (who is usually more into menarche than monarchy) for an unrelated project which will forever be a mystery to you, but you should check out her work on menstruation (which should not be a mystery) because it’s bloody good.
That’s all for now, but Joey is working on some incredible cover versions of songs which I look forward to sharing.
∎
A few mathematical numbers
Posted in News on August 14, 2023
My last post had Joey Marianer (to whom I was flabbergasted to be married) singing some lyrics I wrote, and mentioned that we would soon be at the MathsJam Annual Gathering, and that I’d uploaded all my JoCo Cruise footage for that year. Well, in my aperiodic compiling of blog entries, I have reached a familiar local pattern. Joey (to whom I am still gobsmacked to be married) has sung more lyrics I wrote, we are once again planning to go to the MathsJam Annual Gathering, and I have uploaded all my JoCo Cruise footage for 2023.
A Cake of Sets
At my first MathsJam Annual Gathering, I gave a talk involving one poem I wrote and several that I found. At the 2019 Gathering, Joey and I participated in the competition competition with a Hallelujah competition. At last year’s Gathering, we added some set theory to the Bakeoff with this (cheese(cheesecake)cake) Venn diagram:
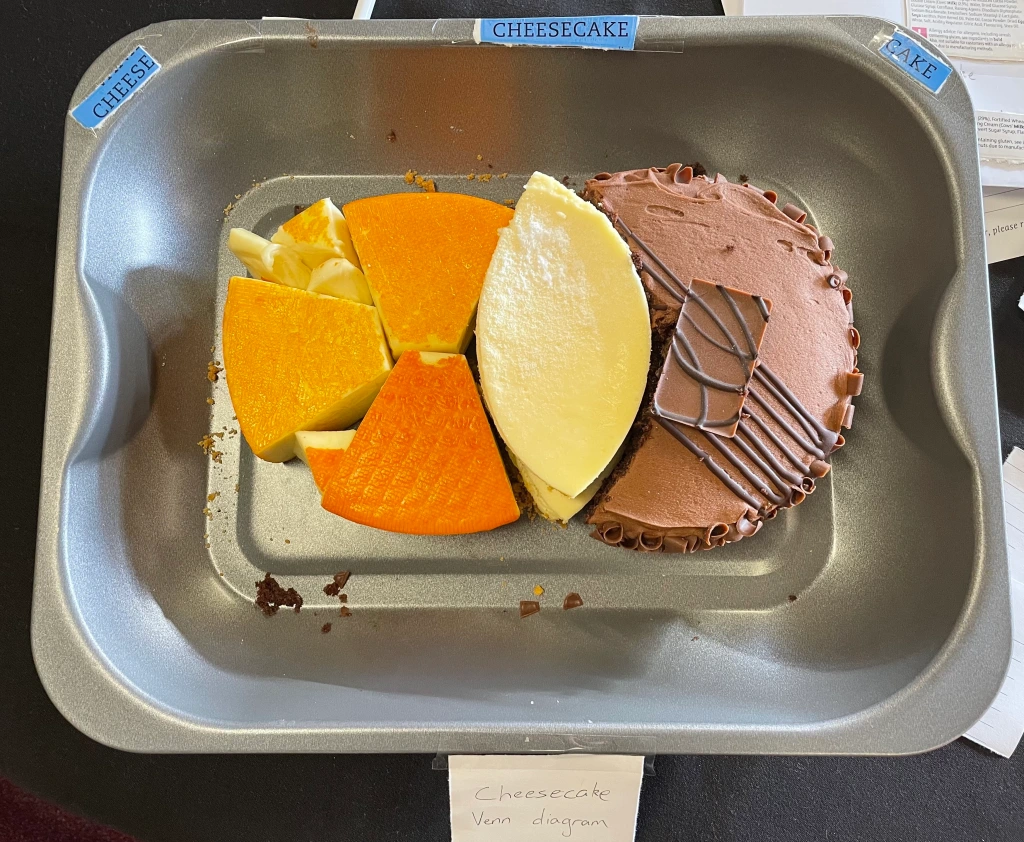

It was mentioned in this excellent summary TikTok by Ayliean!
We assembled it on-site from store-bought cheese, cake, and cheesecake. What with travelling internationally to MathsJam, it would have been impractical to (cheesemake(cheesebake)bake) it ourselves.
A Set of Songs
At this year’s MathsJam, we will add to the set list of the MathsJam Jam.
Symmetry
To start with, we noted an existing theme of symmetric relations in the lyrics of The Beatles’ song ‘All You Need is Love’ and made it explicit. Here’s Joey singing our parody, Symmetry:
Here are the lyrics:
Symmetry!
Symmetry!
Symmetry!There’s nothing that is x that x is not
No ex where you’re not an ex they’ve got
The symmetry says that the relation goes both ways
It’s easy!If you’re my sibling, I’m your sibling too
You’re married to me and I to you
Each of these relations is the same as its converse
It’s easy!x relates to y
x relates to y
x relates to y, why? ’cause y relates to xIf one real number’s greater than the other
Or maybe I’m your son and you’re my mother
Such relations exist, but symmetric ones top our list
They’re easierWhen x relates to y
x relates to y
x relates to y and y relates to xx relates to y
x relates to y
x relates to y, why? ’cause y relates to x
Seven Bridges (of Königsberg) Road
I’ve also written a first draft of a parody of the Steve Young song ‘Seven Bridges Road‘ about the Seven Bridges of Königsberg. Joey hasn’t sung this one, but I intend to enter it into the MathsJam Jam songbook (where there is already a parody of ‘Lola’ about the same topic.) Here are the lyrics:
There are rivers in Königsberg
Cross them as you go
Don’t forget one and don’t you repeat
On the Seven Bridges Road
Now each land mass must have odd or even
Bridges to and fro
Arrive but don’t leave in the same way
And Euler’s work did show
Sometimes there’s an odd one out
How to turn from there and go?
No way for a path with these few rules
Down the Seven Bridges Road
There are rivers in Königsberg
And if ever you decide you should go
There is a way by backtracking only
Down the Seven Bridges Road
Note, this is purely based on the way Jonathan Coulton and Paul and Storm sing Seven Bridges Road when they’re not pretending to be tone-deaf. If other artists sing it differently, the prosody might not work out as well.
This Tiling Never Repeats (in progress)
I’m also working on a parody of History Never Repeats by Split Enz called This Tiling Never Repeats, about the recently discovered aperiodic monotiles, which I am sure will be a big feature of this year’s MathsJam. I expect there to be at least three sets of aperiodic monotile cookies entered in the Bakeoff. I’ve only just started with this parody, but figured I’d mention it in case anyone wants to give me ideas for it, encourage me to finish it, or even write their own. I don’t mind who writes it as long as it exists and is sung at MathsJam.
A Song of Cakes
This section title is just for completeness, and because I needed something to separate the last song from the outro. I know too many songs about cakes to pick one.
As many people contemplate the value of X, I’ve created an account at what is obviously the best-named Mastodon server, Mathstodon. Feel free to follow me there! I don’t know yet how frequently I will post on it and/or my Twitter profile, but at least now you know where to find me if you’re on those networks.
∎
Joey sang some more parody lyrics I wrote, and another Hallelujah
Joey Marianer (to whom, and I cannot stress this enough, I am 💖married❣️) was asked to sing some computer-related songs at a company all-hands meeting, and chose The Bad Coder’s Favourite Things (one of several parodies I’ve written of ‘My Favourite Things’) as one of them. It’s the third one, after Joey’s own ‘Inbox Zero’ (a new addition to our growing list of Hallelujah parodies) and Les Barker’s ‘Reinstalling Windows’ (a parody of ‘When I’m Cleaning Windows’.)
Enjoy!
In other news, we’ll be at MathsJam Annual Gathering in November, which will be a hybrid in-person (in the UK) and virtual event this year. If you like maths, or if you think you don’t like maths but want to find out why people do, or even if you just like parody songs about maths, and the time zone and/or location work for you, I highly recommend joining.
Also, surprise! I thought I’d uploaded all my JoCo Cruise 2022 footage, but I’d somehow missed the Monday concert, with Jim Boggia and Paul and Storm. You can watch it as a single video or a playlist of songs. This means I’ve uploaded more than 22 hours from that cruise, all-up.
And, double surprise (which I of course remembered a minute after publishing this post) Joseph Camann made a musical version of my performance of ‘The Duel‘ on JoCo (virtual) Cruise 2021. I love it!
Linguistic Alternative Polka (“Weird Al” Yankovic parody lyrics)
Posted in News on June 16, 2022
Here are some linguistics-related parody lyrics I wrote to “Weird Al” Yankovic’s “Alternative Polka”. I’ve grouped them into numbered topics, with notes below explaining what each part is about. The topic switches don’t necessarily match the transitions between song snippets in the original.
- Soy un perdedor
‘I’m a loser’, baby,
it means that in Spanish.
Everybody!
Soy un perdedor
‘I’m a loser’, baby,
it means that in Spanish.
Hey
- I am, I am, I am
I said I wanna get copular
I said I’m gonna be copular
You said “Hi, copular, I’ll be your dad.
Be your dad.”
- I know you know what’s on my mind
I know the deixis in my mind
You know the referent that’s inside
I know you know, you know, you know
- Here’s a wug, a wug, a wug, a wug
Here’s a wug, a wug, a wug
A word I never knew, this should be fun!
How do I deal when it’s not the only one?
Now that there are two, it’s twice as fun!
How do I deal when it’s not the only one?
Don’t know what to do, there’s more than one!
Until I pluralise with linguistic morphological smarts
- Help me, my Broca part is broken
Help me, I’ve got no fluent speech
Help me, I understand but hard write speak
Help me, word brain frustrate myself
- Don’t wanna [animal noise]-talk like an animal
I want a squeal with morphemes inside
Don’t wanna [animal noise]-talk like an animal
- So here’s how this bit is fraught:
This rhyme relies on caught-cot.
Hey, hey, hey
- You slang slang slang slang slang
shame shame shame
But slang slang slang slang slang
is everything so let it go.
‘Cause the standards you preach
that that my speech doesn’t reach are so recent that they
ignore etymology, yo!
And every time I speak you chide;
do you know when you scold me
the old meanings did expand, also panned,
yet we understand!
And I’m here to remind you
of the complex ways language got that way
It’s not fair to deny me
of the force of change that still acts today.
You oughta know
Hey
Despite all your rage, language still has to constantly change.
Despite all your rage, language still has to constantly change.
And someone will say something “wrong” that’s right the next day.
Despite all your rage, language still has to constantly change!
- I hate all the ‘u’s
from lands of old.
I hate -our language too
when you write o-u-r.
I don’t o-u anything!
I don’t o-u anything!
I don’t o-u anything!
I don’t o-u anything!
- Language sounds, all around,
watch how they compound!
Language sounds, all around,
they abound.
Language sounds, language sounds
they confound
language sounds, language sounds
so unsound!
language sounds, language sounds
Do you have the time to listen to my rhyme?
Sounds similar and different all at once.
That is one of those minimal pairs that show
phonetic contrast also is phonemic.
A dozen ways to say a /t/
Sometimes my ears play tricks on me
I’m stuck on this grey tape; I think I’m a great ape
Are these distinct phonemes, or allophones?
Are they allophones?
Hey!
Here’s my explanation of the different parts. Please note that while I do have a Masters in Linguistics, I am in no way an expert on any of these things (though I’m pretty sure about the Spanish), so don’t take my word for it.
- Pretty self-explanatory, really. ‘Soy un perdedor’ is Spanish for ‘I’m a loser’. All I changed from the original was the punctuation and the explanation, ‘It means that in Spanish.’
- Copulas and copular verbs link the subject of a sentence to a complement, which can be all sorts of things, including both nouns and adjectives. So the copula ‘am’ in “I am hungry” is followed by an adjective, but it could just as well be followed by a noun. This gives rise to the popular ‘dad joke’ format:
Kid: I’m hungry.
Dad: Hi, Hungry; I’m Dad.
I feel like the copular sense of the verbs ‘feel’ and ‘look’ also have a role in this format of dad joke, though I’m not sure how to properly describe it linguistically:
Kid: I feel like an ice cream.
Dad: Well, you don’t look like one!
(You, as a dad: Well, you don’t look like the copular sense of the verbs ‘feel’ and ‘look’ also have a role in this format of dad joke, though I’m not sure how to properly describe it linguistically!)
But I suppose that’s really just two distinct meanings of the phrasal verb ‘feel like‘, and an implicit ‘eating’ in the Kid’s sentence, which the Dad ignores. Still, you can see how ‘look’ is copular in sentences such as ‘I look weird’. For most verbs, e.g. ‘sing’, you’d have to say ‘I sing weirdly‘, but with ‘look’ it’s just a more specific way of saying ‘I am weird’. We can veer back into dad joke territory when we use a word such as ‘well’ that can be either an adverb or an adjective:
Kid: You look well!
Dad: That’s because I have good eyesight.
Here, the Kid is using ‘look’ as a copula, and ‘well’ as an adjective meaning ‘healthy’, so the phrase means that the Dad appears to be healthy, but the Dad is interpreting ‘look’ as a regular verb and ‘well’ as an adverb, such that the phrase means he’s good at looking at things.
This is more than I expected to say to complement this subject. See also the explanation of #9 for an example of the zero copula as used in African American Vernacular English. - Deixis is when the same word can mean different things depending on context, such as who’s saying the word, when and where they’re saying it, where they’re pointing, and so on. Joey and I made a video demonstrating personal deixis. This lyric just expresses that we only tend to use deixis when we’re pretty sure whoever we are communicating with knows what the deictic words are referring to.
- This refers to the Wug Test — a test of how well a young child understands the rules of their language. The titular example is when a child is shown a picture of a cute little creature and told it is called a ‘wug’. The child is then shown two of them, and asked what they are called. If they understand how words are usually pluralised in English, they’ll answer ‘wugs’. Wugs are very popular with linguists. They are the reason that if I ever record a sequel to my album Wake Up Gasping, it will have to have the same acronym.

- Broca’s Area is a part of the brain involved in language production. A person whose Broca’s area is damaged may have Broca’s aphasia, where they can generally understand writing and speech or signing but have difficulty producing language themselves, usually missing out grammatical function words. I’ve tried to mimic this kind of language in the last two lines (to the extent that the song allows). I hope that this is a somewhat realistic example and not seen as making fun of people with any form of aphasia. I watched some videos by Sarah Scott and Mike Caputo to get an idea of how people with Broca’s aphasia speak and how hard they work to improve their communication.
- Morphemes are the smallest units of language that carry some kind of meaning. For instance, ‘mean’ and ‘ing’ are separate morphemes. A single morpheme can be made up of multiple sounds, but those sounds don’t mean anything by themselves. This is called ‘double articulation‘, and it’s one of the properties of human language that doesn’t tend to exist in animal communication. In fact, perhaps it would point out that difference better to say ‘I want a squeal with phonemes inside’. But we have phonemes in part #10.
- This is what started me writing this ridiculous thing, back in October 2020. The original lyrics are:
My whole existence is flawed.
You get me closer to God.
which got me thinking about how that very couplet is flawed — it doesn’t rhyme in my accent. It relies on the cot-caught merger, where the vowels in the words ‘cot’ and ‘caught’ are pronounced the same. ‘Flawed’ has the same vowel as ‘caught’, and ‘God’ has the same vowel as ‘cot’. In accents with the cot-caught merger, those are both the same vowel, so ‘flawed’ rhymes with ‘God’ and ‘fraught’ rhymes with ‘cot’, but in accents without the merger, those are two different vowels, so the rhyme doesn’t work. You can explore other rhymes that depend on the cot-caught merger and other accent-specific features in Rhyme.Science, the rhyming dictionary I made. - Some nice people like to ‘correct’ others for using words differently from how they do. Sometimes they take exception to usages they consider ‘new’, but don’t realise have been around for hundreds of years. Sometimes they happily use words and grammar that were considered incorrect much more recently. Sometimes they call things ungrammatical because they’re using the grammar of a different dialect. Sometimes they try to use the etymology of a word to dictate how it should be used today. In all of these cases, if they knew more etymology, they’d understand that everything we say comes to us via previously-pooh-poohed mistakes, mispronunciations, dialectal or regional variations, calques, borrowings, slang, analogies, generalisations, specialisations, misunderstandings, rebracketings, back-formations, metaphors, and so on. There’s not much point trying to stop these processes, though I’m sure somebody tried to stop the language you consider correct today from getting how it is.
To learn more, I can recommend The History of English Podcast, etymonline, Grammar Girl, Lingthusiasm, The Unfolding of Language, and… wait, I should probably stop here before I list the entire contents of my podcast library and the bookcase to my right. Just… take your impulse to quash somebody else’s communication and redirect it towards learning more yourself. - Where my Noah Webster stans at? Here’s an entire song parody I wrote about -or vs. -our spellings.
- Spoken languages have a lot of sounds in them! More sounds than the speakers realise. To figure out what the basic units of sound in a given language (called phonemes, and written between /slashes/) are, you need to find ‘minimal pairs’ — words that only differ by one sound. You can tell that /t/ and /r/ are different phonemes in English, because ‘time’ and ‘rhyme’ are different words. But there are actually many different ways of saying /t/, depending on context, and even though they are distinct sounds (called phones, and written in [square brackets]) they are all perceived as the same /t/ phoneme. This is the case for /r/ and other phonemes as well. The different sounds that are all perceived as the same phoneme in a given language are called allophones of that phoneme.
Note that sounds that are allophones in one language can be separate phonemes in another — for instance, in Spanish, a single phoneme has allophones that English speakers would hear as the separate phonemes /b/ and /v/.
Sometimes we actually can use allophones to distinguish between phrases, though! For instance, we can hear the difference between ‘gray tape’ and ‘great ape’. The difference is called a juncture, and I’ll be honest, I read about it last week on wikipedia and have not read the citation, so I’m really not sure whether this makes them distinct phonemes or still allophones. By the way, humans are in the Hominidae family commonly called the ‘great apes’ (though some uses of that term exclude humans), so if you think that you’re a great ape, you probably are.
This part of the song has another kind of sound — sounding weird! The original song has ‘melodramatic fools’ where I put ‘minimal pairs that show’, and both lyrics have a stress on the second syllable, where it wouldn’t normally go. In this case, all that does is make it sound a bit wrong, but syllable stress can also be phonemic and can differentiate words. For instance, the minimal pair ‘abstract’ (the adjective or noun, with the stress on the first syllable) and ‘abstract’ (the verb, with the stress on the second syllable.) There are many English words which change stress depending on which part of speech they are (convict, record, laminate, attribute, etc…), but in a lot of cases the unstressed vowel also changes to a schwa, so the stress isn’t the only difference.
That’s all I have to say about that! Next, perhaps I’ll finish the entirely unnecessary parody lyrics about PSOLA that I started writing in 2016, so if you’re playing these on a string instrument, stay tuned!
We got married (to each other) and then did cute couple things on a boat!
Posted in News, Performances on April 15, 2022
Remember that time that Joey Marianer and I got engaged (to each other)? Well, a while after that, we also got married, as is typical for engaged couples. It was just a small ceremony in a courthouse, followed by a small gathering with two large cheesecakes. Here’s a very short video synopsis of the wedding:
I just edited the closed captions, and noticed that YouTube’s autocaptions thought the judge said, ‘congratulations youtube and you guys get a blog it’s okay’ when in fact he said, ‘Congratulations, you two. And you guys can applaud; it’s okay!’ Anyway, that video has been gathering congratulations on YouTube for a while, so now you guys get a blog about it.
Then we ate cheesecake with a few friends, and Joey did this:
If you don’t understand what just happened, here’s a video that will explain it.
A few days and two negative COVID tests later, we boarded the JoCo Cruise. On cosplay day we cosplayed each other:

This was mainly to facilitate changing into our pants for the Fancy Pants Parade. I haven’t found a video that shows us in the parade itself, but here’s one of us practising last year, when we thought the cruise might be virtual again so we’d need a video:
Then two days later, all decked out for formal night, we did a show, which was also quite geared towards things we could only do while physically together. I structured the setlist to tell the story of how our relationship developed through collaborating on songs.
If you prefer, there’s also a playlist of individual pieces. I even made a playlist of the videos mentioned in the show, complete with the comments in which I might have been flirting with Joey. Some of the poems and songs are on my album, one is on our album of SpinTunes entries, some are on the playlist of Hallelujahs, but three of them have never been published anywhere before.
I’ve wanted to do a poetry show on the cruise for a while, but was always afraid of having to miss out on other events that were scheduled at the same time as it. I did a show on the 2021 virtual cruise where that wasn’t so much of a concern, and people seemed to like it, so an in-person sequel seemed like a good idea. Only, with Joey’s help, it was not merely a poetry show, but also a musical show!
My fears were somewhat realised; this show was scheduled opposite the reception for frequent cruisers, which most of the people who know me well enough to attend my show were eligible to go to. But the other thing those people know is that I film every event I’m at (so far I’ve uploaded 12 hours, 48 minutes of video from the 2022 cruise, and I’m only up to Wednesday afternoon), so they could safely miss the show and watch it now! We got through the setlist with a little time to spare, so we even got to attend the reception briefly.
How I got to work at CERN (video) and some rambling about video (text)
Posted in Story Time on April 2, 2022
Right before JoCo Cruise 2020, I bought a 256GB SD card, just as a treat, so I wouldn’t have to worry about switching between 64GB cards and offloading videos to my Mac when recording as many events as possible. I discovered too late that my camera (a Nikon P7700) was too old to support 256GB cards, and when I got home from the cruise we were in lockdown, so I couldn’t return the card. This ultimately led to my buying a new camera (a Sony ZV-1) in late 2021 which would support the card, and I am very happy with this application of the sunk cost fallacy.
I planned to test out the camera at a Burning Hell show in Vienna (which would have been my first in-person concert since the cruise), but Austria went back into lockdown, so instead, I recorded myself talking about how I got to work at CERN, as a sequel to That time Steve Wozniak bought me a laptop and That time Steve Wozniak taught me to Segway and then played Tetris and pranks through a concert. I recorded 36 minutes continuously, in 4K, and I ran out of things to say before the camera had to stop for any reason. My old camera would have to stop after less than 30 minutes recording in 1080p, due to the 4GB file size limit, so I’ll call that a success.
Whether my 36 minutes of talking about my route to CERN is worth watching is up to you to decide:
The video is fully closed-captioned by me, a human, so if you prefer skimming text to watching videos, click the … symbol (at the end of the line below the title) and choose Open Transcript.
The Burning Hell are making another attempt at a Vienna show in September, so here’s hoping I can run that original experimental design.
I’ve since been on JoCo Cruise 2022, and found the camera much less stress than my old one for recording concerts. I not only don’t need to change the card as often, I’m also not limited to 4GB files, or by the battery capacity, since it can use an external battery pack. So I’ve recorded most events continuously. The new camera also shows me what it’s focussing on, and I can change that using the touch screen, so from what I’ve seen so far, I haven’t had any incidents of an entire video being out of focus.
The only issue I had with the new camera is that if I start recording video immediately after turning it on, it doesn’t show it’s recording for another second or so, so I’d often press the button again and inadvertently stop recording in my attempt to start recording. In most cases I realised what had happened immediately and start recording again, but in one case I didn’t notice for a while and missed the introduction of a performer.
I used to do most of my lightweight cruise video editing in QuickTime Player, but for whatever reason its ‘Split Clip’ option is disabled for the videos from my new camera, so I’m trying out LosslessCut. It has a few issues, but I’ve found workarounds for them. One great thing about it is when I cut a show into individual parts, it can not only export those parts as individual videos, but also give me a list of times for those parts. I can paste them into the YouTube description of the full video so that they show up as chapters.
With the help of to that feature, I’m uploading most of them as full shows with chapter markers, and putting them into a playlist of the whole cruise as I do so. I’m also splitting shows into individual songs/stories/questions when relevant, and uploading those as separate videos, so I can add the individual pieces to other relevant playlists. Look in the description of any of the full-show videos to find a link to a playlist of the individual parts of the show. It will take a while to get everything processed and uploaded, so subscribe or check back later to see more.
Another thing I did (and recorded some video of) during that trip was marry Joey Marianer, but that can have its own blog post later. If you’re impatient, you can check out the Joey-Angela Merger playlist.
A successful ploy to increase engagement
Posted in News on January 2, 2022
Well, in 2021, among other things, I released an iOS app and a poetry album, wrote an article about accessibility, tech edited three articles about iOS development, won my second Fancy Pants Parade, did a poetry show, wrote a macOS app to find words that look or sound like they’re related but aren’t and a script to make etymological family trees, found a job, lost a job, found a job again, and finally buried a job in soft peat for three months and recycled it as firelighters (that last bit is an exaggeration. Burning jobs to keep warm is not advisable.)
Here’s another exciting thing that happened that I didn’t mention on this blog. During a brief lull in the apocalypse, Joey Marianer came to visit, and we got engaged… to each other! We had of course already discussed this previously, and I wasn’t expecting a song and dance to be made about it, but there was nevertheless a song, as follows:
It’s a parody of the “Weird Al” Yankovic original, “Good Enough for Now“. I find metal rings uncomfortable and a bit dangerous, so Joey got me a silicone engagement ring with a ring on it. This is a much cooler idea than the off-the-shelf ring I got Joey which has flowers on it and no explicit mathematical concepts.
The pretense for recording that was that immediately beforehand, we’d sung some words I’d written to a tune that came to Joey in a dream:
Joey happened to be here while my friend Phil got married (a year later than planned) and joined a group of Phil’s vaccinated and tested friends to celebrate in Tenerife. So here we are walking along the beach looking all couple-y.

I’ll eventually put up videos of some things we saw in Tenerife. After we got back from Tenerife but before Joey went home, we recorded a few short videos in which we are exceedingly cute at each other while demonstrating some linguistic concepts. Here we explore the differences in our accents:
And here we demonstrate how personal deixis can change the meaning of a sentence depending on context:
So, plague willing, we’ll get married in February, have multiple wedding-adjacent cake-eating parties in various real and virtual places over the next several years, and at some point during that time I’ll get the appropriate visa so we can move in together and hopefully only get on each other’s c-tactile nerves.
And now for some unrelated things to look forward to on my YouTube channel. The above videos were shot on my iPhone, which was my first experience with 4K HDR. I’m not sure if editing that on my mid-2014 MacBook Pro did the HDR justice.
However, I bought a new camera recently which can do 4K, and also has several other features which will make recording concerts (and indeed, entire cruises full of concerts) easier — no more stopping to get around a 4GB file size limit, or change batteries, or change SD cards. I won’t generally film entire concerts in 4K due to the space requirements and likelihood of the camera overheating and shutting down, but it’s a nice feature to have for other things. I’ve also ordered the new MacBook Pro, which will have a better display for viewing and editing such video.
I planned to film as much as possible of a concert here in Vienna in 4K, just to see how long I could film continuously in 4K if I took all the measures I knew about to prevent overheating. The concert had to be cancelled due to lockdown, so instead, I recorded myself talking about how I got to work at CERN, as a sequel to the video about getting a laptop from Woz and going to a concert with him. I recorded in 4K for 36 minutes nonstop (which is longer than my old camera can record nonstop even in 1080p) before I ran out of things to say, so I’d call that a successful test. When the new MacBook arrives, I’ll edit that video and hopefully put it online before flying away to get married and (insert SARS-CaVeat here) record an entire cruise full of concerts. I hope I remember how to record and process an entire cruise full of concerts after a year off, and don’t make too many mistakes with the new camera.
Etymological family trees
Posted in News on December 30, 2021
A while ago I found a post about Surprising shared word etymologies, where the author had found words with common origins (according to Etymological Wordnet) which had the most dissimilar meanings (according to GloVe: Global Vectors for Word Representation.) I loved the post, but my main takeaway from it was the The History of English Podcast, linked in the Further reading section. I immediately started listening to that, in reverse order (that’s just the easiest thing to do in the Apple Podcasts app. Back when podcasts were in iTunes, I used to listen to all my podcasts on shuffle, so if you like order, this is an improvement) starting from Episode 148. I’ve since finished it and started listening to something else before I go back for the newer episodes. I was in it for the English, but I also learnt lot more history than I expected to.
The diagrams
Back in October, hearing about how yet another absurd list of words all derived from the same root word (I think in this case it was bloom, flower, phallus, bollocks, belly, flatulence, bloat, fluid, bladder, blow, and blood from episode 62) I decided I couldn’t just listen to these ridiculous linguistic family trees any more; I had to see them. As you might have seen in previous posts, my go-to for creating that kind of diagram is using AppleScript to control OmniGraffle. So I wrote an AppleScript to make tree diagrams showing words that are all derived from the same root word(s) as a given word. Before I bore you with the details, I’ll show you a little example. This is what it gave when I asked for the English word ‘little’.

The root word is in a blue oval, the words in the same language as the one I asked about (in this case, English) are in brown rounded rectangles, and the words in other languages are in black rectangles. I thought about having a different colour and shape for each language, and a legend, but decided to keep things simple for now.
Image descriptions
The script also generates a simple image description, which I’ve used in the caption. I intended it for use as alt text, but some of these diagrams are difficult to read at the size shown, so even people who don’t use screen readers can benefit from the description. You can also click on any diagram for a full-sized pdf version.
It doesn’t describe the entire structure of the tree (I’m trying not to get distracted researching nice ways to do that for arbitrary trees!) but it’s probably better than nothing. It only lists the words in the language you asked about (assuming that is English), since English screen readers likely wouldn’t read the other ones correctly anyway. It might be cool to autogenerate sound files using text-to-speech in voices made for the other languages and attach those to the nodes to enrich the experience when navigating through them in OmniGraffle or some other format it can export, but that’s a project for another day.
On the subject of accessibility, I’m happy that the History of English Podcast provides transcripts, so I can easily find the episodes relevant to some of these diagrams.
Simplifying the diagrams
Sometimes the diagrams get crowded when a lot of words are derived from another word in the same language, or a lot of other languages derived words from the same word. I wrote a second script to group words into a single node if they’re all derived from the same word, don’t have any words derived from them, and are all in the same kind of shape as the word they’re derived from. That last constraint means that if you searched for an English word, English words all derived from the same English word will be grouped together, and non-English words all derived from the same non-English word will be grouped together, but English words derived from a non-English word (or vice versa) are not, because I think they are more interesting and less obvious.
It’s actually quite satisfying to watch this script at work, as it deletes extra nodes and puts the text into a single node, so I made a screen recording of it doing this to the diagram of the English word ‘pianoforte’. I’m almost tempted to add pleasant whooshing sound effects as it sweeps through removing nodes.
The data
Words and their etymologies
The data from Etymological Wordnet comes as a tab-separated-values file. AppleScript is best at telling other applications what to do, not doing complicated things itself, so I left all the tsv parsing up to Numbers, and had my script communicate with Numbers to get the data. The full data has too many rows for Numbers to handle, but I only needed the rows with the type rel:etymology, so I created a file with just those rows using this command:
grep 'rel:etymology' etymwn.tsv > etymology.tsv
then opened the resulting etymology.tsv file in Numbers, and saved it as a numbers file. This means missing out of a few etymological links (some of which are mentioned below), but it’s good enough for most words.
The file simply relates words to the words in the first column to words they are derived from in the third column.
Languages
Each word is listed with a language abbreviation, a colon, then the word. The readme that comes with the Etymological Wordnet data says, ‘Words are given with ISO 639-3 codes (additionally, there are some ISO 639-2 codes prefixed with “p_” to indicate proto-languages).’ However, I found that not all of the protolanguage codes used were in ISO 639-2, so I ended up using ISO 639-5 data for protolanguages and ISO 639-3 data for the other languages, both converted to Numbers files and accessed the same way as the etymology data.
The algorithm
The script starts by finding the ultimate root word(s) of whatever word you entered. It finds the word each word is immediately derived from, then finds the word that was derived from, and so on, until it gets to a word that doesn’t have any further origin. Some words have multiple origins, either because they’re compound words, homographs, or just were influenced by multiple words, so sometimes the script ends up with several ultimate root words. This part of the script ignores origins that have hyphens in them, because they’re likely common prefixes or suffixes, and if you’re looking up ‘coagulate’, you’re unlikely to want every single word derived from a Latin word with a prefix ‘co-‘.
For each of the root words, the script finds all words derived from it, and all words derived from those, and so on, and adds them to the diagram.
The code
In case you want to try making your own trees, I’ve put the AppleScripts and the Numbers sheets used for this in a git repository. It turns out having the version history is not terribly useful without tools to diff AppleScript, which is not plain text. It is possible to save AppleScript as plain text, but I didn’t do that in the beginning, so the existing version history is not so useful. It looks like AS Source Diff could help.
There are a lot of frustrating things about AppleScript when you’re used to using more modern programming languages. Sometimes that’s part of the fun, and sometimes it’s part of the not-fun.
Trees from Surprising Shared Etymologies
I tried making diagrams of some of the interesting related words mentioned in The History of English Podcast, such as the one with flower, bollocks, phallus and blood mentioned earlier, but the data usually didn’t go back that far. So I tried the ones mentioned in the Surprising shared etymologies post, because I knew they were found in the same data. In several cases I found the links didn’t actually hold up, as the words were descended from unrelated homonyms. I’ve done my best to figure out which parts of these trees are correct, but can’t guarantee I got everything right, so take this information with a grain of research.
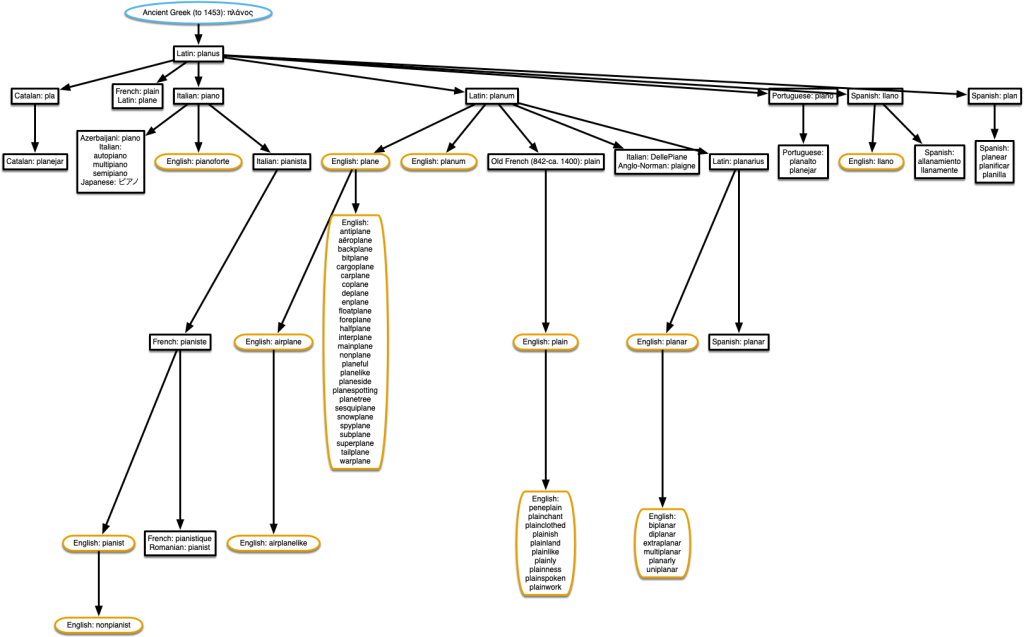
“piano” & “plainclothed”
This was a bit of a puzzle, because there is actually no origin given in the data for English word ‘piano’, although it is given as the origin of many words in other languages. But their example in the ‘datasets’ section shows English: pianoforte, so I used that instead.
I could have added a row to the spreadsheet linking English ‘pianoforte’ with English ‘piano’, and then the many words in other languages that derive from English ‘piano’ would have shown in the diagram as well. Click on the diagram for a pdf version.
“potable” & “poison”
Also potion! According to the data, Latin potio is derived both from Latin poto, and from Latin potus, which is itself derived from Latin poto. The word is its own niece! I had to make a change to the script to ensure there wouldn’t be double connections in this case.

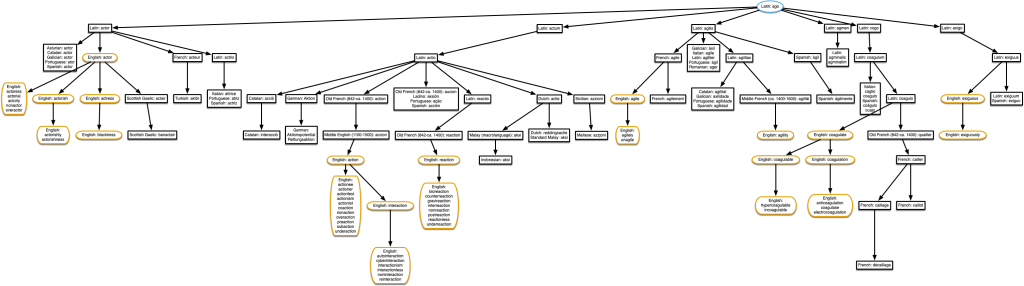
“actor” & “coagulate”
Agile and exiguous, too! It’s starting to get a bit complicated.
“estate” & “contrast”
This tree also includes ‘prostate’, but only ‘pro-state’ (meaning favouring the government) derives from English ‘state’ as shown here. Prostate the body part is actually related, but only if we go back to the Proto-Indo-European root *sta-, which is not in the Etymological Wordnet data. Since the data doesn’t distinguish between the two meanings of ‘prostate’, this tree erroneously includes prostatectomy and cryoprostatectomy, a procedure I was happier not knowing about.
If you think it’s surprising that ‘estate’ and ‘contrast’ are related, have a look at other words derived from *sta-. Understand, obstetrics, Taurus, Kazakhstan… if Etymological Wordnet had that data, this tree would resemble Pando.

“pay” & “peace”
This one comes up in episode 59 of the podcast — the word ‘pay’ literally meant ‘make peace’. It’s not too hard to imagine how paying someone would pacify them. The diagram is incorrect though. ‘Peace’ is shown as being derived from Middle English pece. This is actually the source of ‘piece’, but not ‘peace’. As far as I can tell, pece (and therefore also ‘piece’) shouldn’t even be in this tree. The word ‘peace’ is derived from Middle English pees, near the middle of the diagram, so it is still related to ‘pay’.

“cancer” & “cancel” & “chancellor”
As explained in episode 99 of The History of English Podcast, chancellor is just the Parisian French version of the Norman French canceler. The word ‘cancel’ didn’t come from ‘canceler’, though — ‘cancel’ and ‘chancellor’ both come from a word meaning lattice, whether the lattice a chancellor stands behind, or that of crossing something out to cancel it. The same word also give rise to ‘incarcerate’, but that link is not in the data.
As far as I can tell, these are not actually related to the English word ‘cancer’, though. There are two unrelated Latin words ‘cancer’, one meaning ‘lattice’, and the other meaning ‘crab’, and thus crab-like cancer tumours.

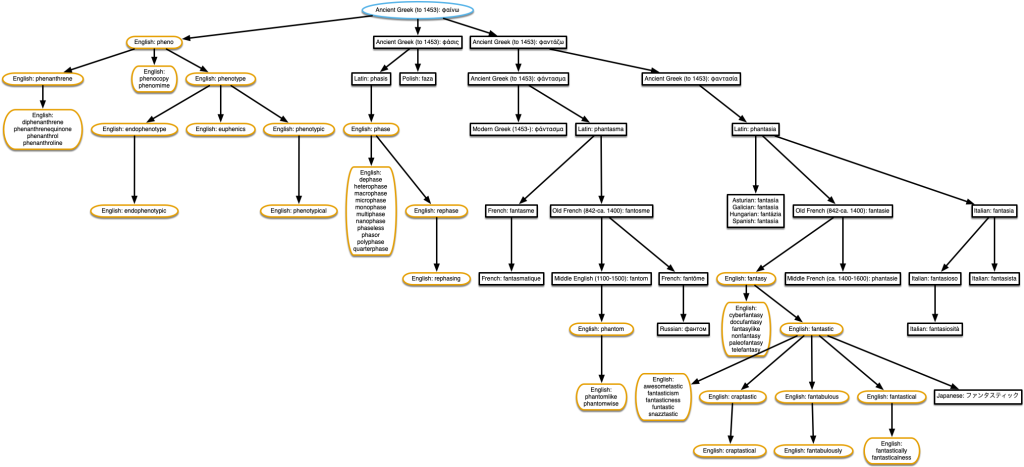
“fantastic” & “phenotype”
This also shows that ‘craptastic’ is related to ‘phasor’. Sometimes the best things about these are the lists of derivative slang words.
“college” & “legalize”
Also ‘cull’, ‘legend’, and ‘colleague’.

“lien” & “ligament”
‘Cull’ should not be in this diagram, as it’s related to a different homonym of Latin colligo. See the ‘Limitations‘ section below.

“journal” & “journey”
Surprising shared word etymologies says:
While it seems like “journal” and “journey” should be close cousins, their nearest common ancestor is in fact quite old – the Latin “diurnus”, meaning “daily”.
This seems about right from the data, and I’m surprised they didn’t both come from the Old French jor. My dictionary of French etymology doesn’t list the French versions of either word.

This is the tree I get if I start from the word ‘journal’. If I start with ‘journey’, it shows that Latin diurnum is also given as an origin of Old French jor, but this adds a lot of complication to the tree and only one extra English word, ‘abatjour’.
“educate” & “subdue”
I’m not sure how they got these two, to be honest. They may indeed be related, if, as etymonline says, subdue came from the same root as subduce, and subduce and educate came from Proto-Indo-European *deuk- (or *dewk-, as wiktionary spells it). There’s a lot about other words from that root (not including ‘subdue’) in episode 85 of the podcast.
I don’t know how they got this from the Etymological Wordnet data, though. Etymological Wordnet was extracted from an older version of wiktionary, and it doesn’t have very many Proto-Indo-European roots. The post says that ‘subdue’ comes from the latin subduco, meaning ‘lead under’. But even looking at all the data (not just the rows with ‘rel:etymology‘), ‘subdue’ is only linked to other English words. Perhaps they were looking at ‘subduce’ instead.
The post also says they both come from Latin duco. If I look at all the data, I can get to Latin duco from ‘educate’ (via Latin educatio and educo.) But looking more closely at that link on wiktionary (the source of Etymological Wordnet’s data) it seems there are two meanings of Latin educo, one coming from Latin duco and one coming from Latin dux, and it’s the dux origin that seems more relevant to education. However Proto-Indo-European *deuk- is the hypothetical source of dux, so that’s how it relates to subdue.
I’m getting a bit lost following these words around wiktionary and etymonline. I believe they’re related, but I’m not sure if they’re related via Latin duco, and I haven’t a clue how the relationship was found in the Etymological Wordnet data (I should probably read and/or run their ruby code to find out), so I can’t generate even an erroneous family tree of it.
Limitations
Did you notice that the word ‘cull’ shows up in both the tree for ‘college’ and the one for ‘ligament’? Does that mean that ‘ligament’ is also related to ‘college’? Nope. The issue here is that the Latin colligo has two distinct meanings with different origins, one via Latin ligo, and one via Latin lego. ‘cull’ derives from the ‘bring together’ meaning of colligo, which derives from lego, so it’s actually not related to ‘ligament’. Only one origin for colligo is shown on each of these two trees, since neither ‘college’ nor ‘ligament’ are derived from colligo, so the script only got to colligo when coming down from one of the ultimate root words, rather than when going up from the search word. But if we create a tree starting with the word ‘cull’, it gets both origins and the resulting tree makes it look like ‘college’ and ‘ligament’ are related.

Since the data only has plain text for each word, there’s no way for the script to know for sure that colligo isn’t one word with multiple origins (like ‘fireside’ is), but actually two separate words with different origins. And there’s no way for it to know which origin for colligo happens to be the one that ultimately gave rise to ‘cull’.
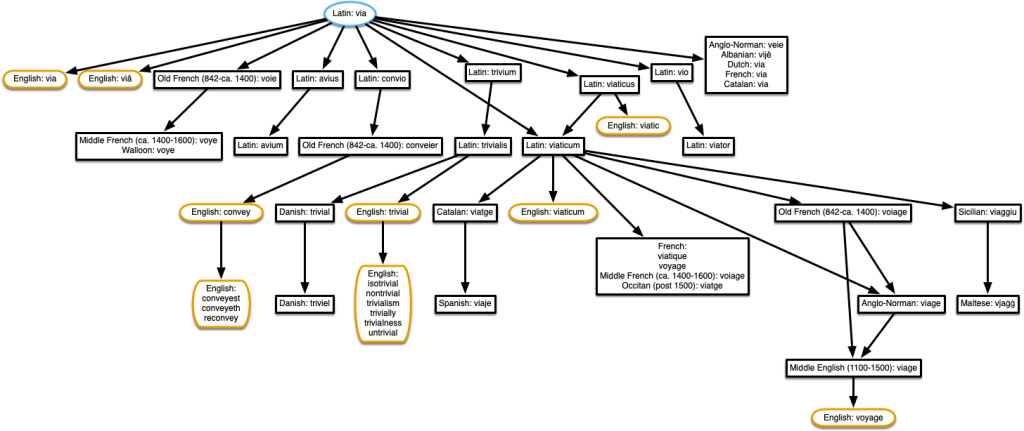
A trivial example
I’ll leave you with a tree I found while looking for a trivial example to show at the beginning. Here’s the tree for ‘trivial’. There are many more related words given in episode 37 of The History of English Podcast.